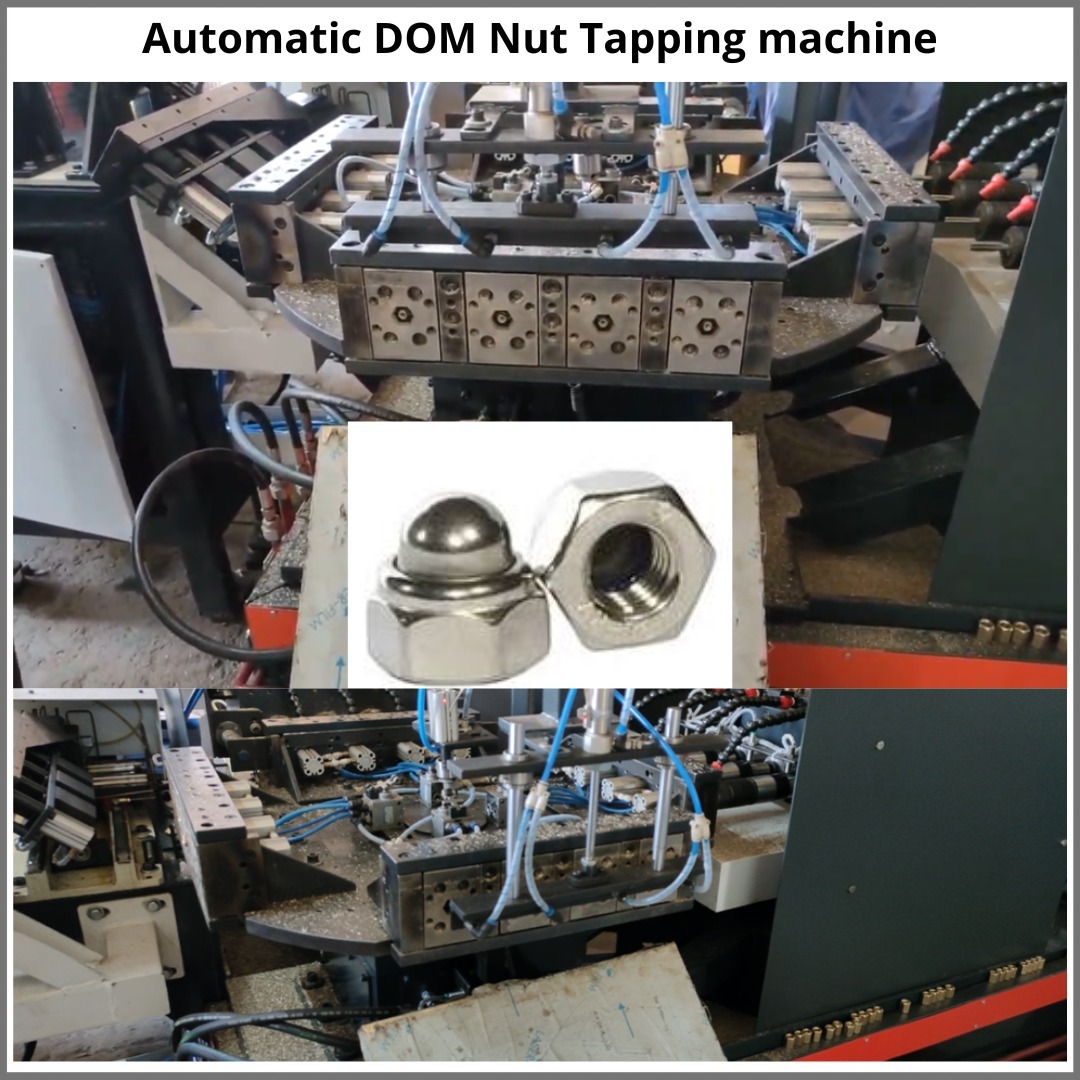
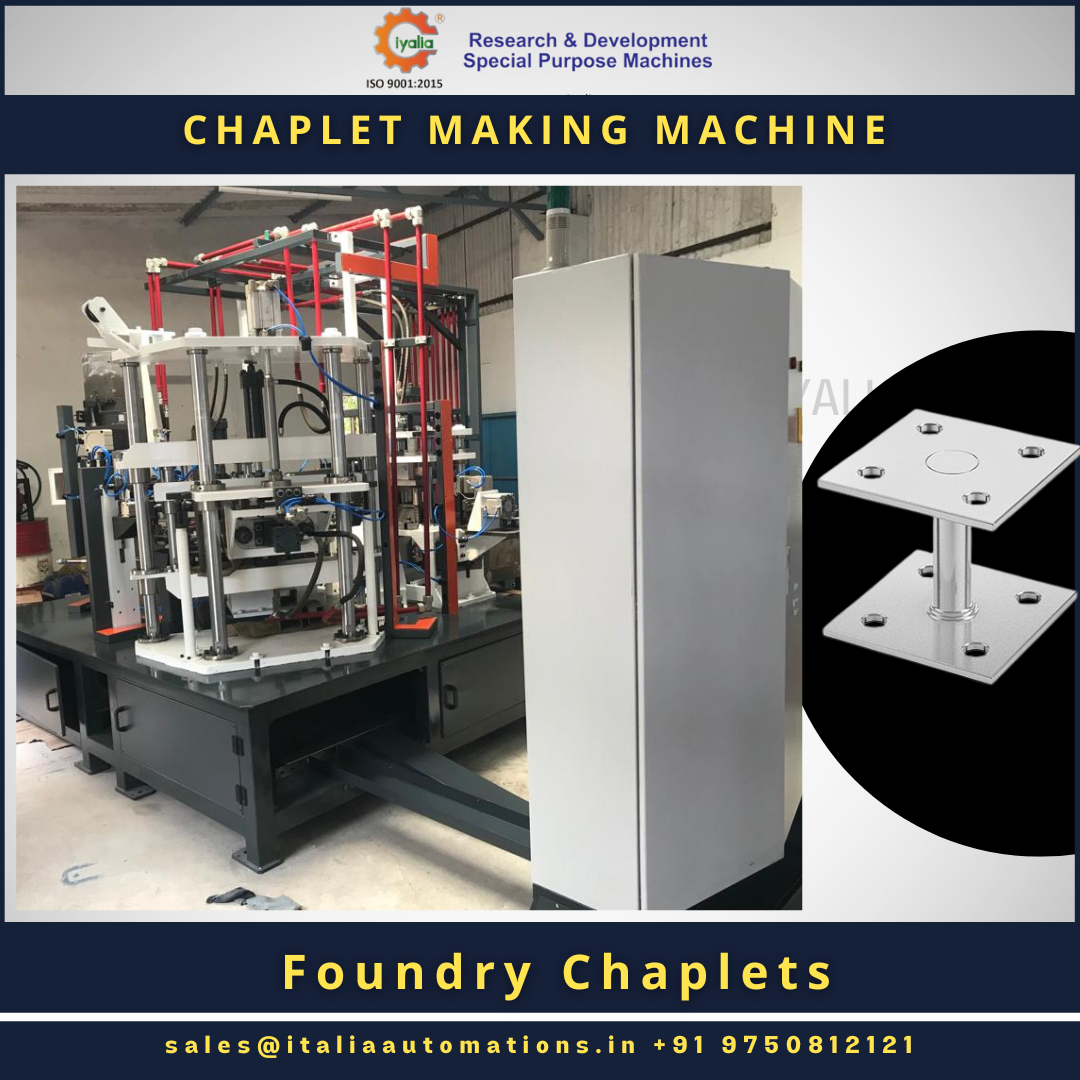
Forging Automation robotic for the cold forging industry
Forging is a process of shaping metal by applying force while it is solid. Cold forging is a type of forging that is done at room temperature, unlike hot forging, which is done at high temperatures. Cold forging is used to make various parts, such as gears, bolts, and rivets.
Automation and robotics can be used in the cold forging industry to increase efficiency and productivity while also improving safety. Here are some potential ways that Automation and robotics could be implemented in the cold forging industry:
Automated material handling: Automated systems could be used to transport raw materials and finished parts throughout the forging process. This could reduce the need for manual labour and increase efficiency.
Robotic forging machines: Robots could be used to perform the actual forging process. They could be programmed to apply precise amounts of force to the metal, resulting in consistent and high-quality parts.
Quality control: Automated systems could be used to inspect finished parts to ensure that they meet the required specifications. This could reduce the need for manual inspection and improve the overall quality of the parts.
Data collection and analysis: Automated systems could collect data throughout the forging process, including information about temperature, pressure, and other variables. This data could be analyzed to identify opportunities for process improvement and optimize the process's overall efficiency.
Implementing Automation and robotics in the cold forging industry could significantly impact efficiency, productivity, and safety. However, it would require significant equipment, software, and training investment. Additionally, it is important to evaluate the potential impact of Automation on the workforce carefully and to develop strategies to mitigate any negative effects.
Keywords
type
need
bolts
gears
force
metal
safety
rivets
Robots
robotics
pressure
software
required
analysis
consistent
strategies
information
hot forging
productivity
opportunities
various parts
raw materials
manual labour
specifications
finished parts
potential ways
Data collection
precise amounts
Quality control
overall quality
other variables
room temperature
potential impact
negative effects
high temperatures
Automated systems
manual inspection
high-quality parts
Automation robotic
overall efficiency
process improvement
training investment
significant equipment
cold forging industry
actual forging process
Implementing Automation
Robotic forging machines
Automated material handling